Artificial intelligence is intelligence that is not of biological origin, but demonstrated by artificial machines and algorithms. In practice it encompasses a large collection of methods that give rise to some form of intelligent behavior. The recent surge in interest in AI is mainly caused by the success that different self learning algorithms have shown on various tasks that humans typically perform, such as recognizing objects.
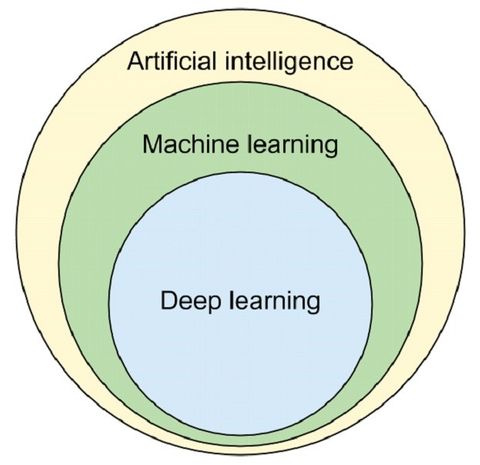
Machine learning is the collective name of these learning based methods and drives most of the AI applications in use today. A machine learning algorithms typically receives some data as input (for example an image), then performs some internal computations and provides on output (for example a class to which the image belongs). By getting feedback about whether the image was classified correctly the algorithm will learn and become better at the task. Eventually an algorithm can become so good at a task that it even outperforms humans.
Deep learning is a subset of these learning based algorithms that makes use of multiple 'layers' of computations, hence the adjective 'deep'. These deep learning algorithms are also called 'neural networks', referring to their similarity to how biological brains work. These algorithms are particularly successfull on highly structured data such as images, text, audio, etc.
During the course we will explain the similarities and differences between machine learning and deep learning and how to choose which one you need for your application. You will get an overview of the most common machine learning and deep learning methods that are being used and how to determine which method is best suited for a particular data set and a certain task. Furthermore you will get an understanding of the basic principles underlying these methods and learn how to actually train an algorithm during the practicals.
Applications
Large amounts of data play an increasingly important role in healthcare. Medical images, health records, DNA sequences, ICU recordings, all these data streams form an increasing challenge for medical professionals to accurately interpret and extract relevant information from and new technologies to record data from patients keep emerging. Artificial intelligence can support healthcare professionals in interpreting all this data and help them provide the best care for their patients. There are several areas in healthcare where AI applications start to play a role.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is one of the leading fields that is using AI algorithms to interpret their data. Deep learning has from the start been very successfull in interpreting images, so it has been an obvious step to apply these techniques to medical images. These algorithms are very helpful for recognizing all kind of pathologies in medical images and are already performing similar to humans in several cases. Applications can be diverse, from assisting in the planning of surgical interventions, to assessing the quality of pathological samples or providing a second opinion for clinicians.
Text mining
Health records contain a lot of information, but can be time consuming to read. AI can help extracting relevant information from large amounts of text and give both researchers and clinicians insight into a patients medical history. Conversely, AI can help patients to interpret their own records by translating difficult jargon into everyday language.
Genetics
The human genome is made up of an incredible amount of genes. The smallest defects in these genes can have far stretching consequences, but finding which defects cause which pathology is like searching a needle in a haystack. Recently, some impressive advancements have been made to better sequence genomes by using AI, paving the way for genomics researchers to discover new genetic disorders.
ICU recordings
On the ICU, large amounts of data are continuously recorded. Heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, all these parameters can contain important information about a patients condition, but continuously interpreting them is unfeasable. AI algorithms, however, can continuously monitor these vital signals and give warning signals when abnormalities occur, enabling early detection of patient deterioration.
During the course we will cover the most important areas of healthcare where AI applications are currently being implemented. This provides participants a dive into AI in their own medical domain, but also an overview of how AI is being used in other medical domains.