This is an AI for Health MSc project. Students are elgible to receive a monthly reimbursement of €500,- for a period of six months. For more information please read the requirements.
Clinical problem
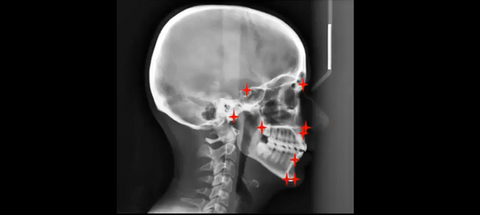
In Orthodontics, a lateral headplate (or cephalogram) is one of the diagnostic tools, used to compose an orthodontic diagnosis. On this lateral headplate a cephalometric analysis is performed to get an idea of facial growth, upper and lower jaw position and inclination, position and inclination of the teeth and soft-tissue position. This cephalometric analysis usually consists of at least 30 points and will result in different angles and distances, from which an orthodontic diagnosis can be made. Today these cephalometric analyses are performed manually, which takes about 5 minutes per patient. In a normal orthodontic office, about 15-20 cephalometric analysis are performed per week. So, this costs the orthodontist 75-100 minutes every week. If this process can be automated by an AI model, this will save the orthodontist a lot of time.
In a pilot study, promising results were obtained on a limited set of landmarks. In this project the student will build a model to reliably place all 30 landmarks and calculate the relevant angles for orthodontic diagnosis, thereby saving manual annotation time for orthodontists.
Solution
The AI solution will be a neural network, that can place the landmarks as good as trained experts. This algorithm should also determine the distance between the landmarks and calculate angles between multiple landmarks. The final outcome will be an application that produces a list of landmark distances and angles.
Data
The data consists of 1000 lateral headplates (x-rays), made at the department of Dentistry - Orthodontics and Craniofacial Biology. The landmarks will be determined by 2 trained experts, in the grand challenge platform. From the grand challenge platform the data can be exported for further analysis.
Embedding
Students will be supervised by an orthodontist from the department of Dentistry, Orthodontics and Craniofacial Biology, with clinical expertise and a research scientist from the Radboud Technology Center, with extended expertise in deep learning. We provide access to a large GPU computation cluster. The final deliverable is a code repository on GitHub and a publicly available algorithm on the platform Grand Challenge or on a separate website.
Requirements
- Student with a major in data science, computer science, or artificial intelligence in the final stage of master level studies
- Interest in (medical) image analysis and machine learning
- Affinity with programming in Python and with deep learning packages (e.g. PyTorch) is required
- Affinity with medical image processing is welcome
Information
- Project duration: 6 months
- Location: Radboud University Medical Center
- For more information, please contact Frits Rangel and Silvan Quax

